Welcome to Iris Biotech
For better service please confirm your country and language we detected.

For better service please confirm your country and language we detected.

Thank you very much for your interest in our products. All prices listed on our website are ex-works, Germany, and may attract customs duties when imported.
You may/will be contacted by the shipping company for additional documentation that may be required by the US Customs for clearance.
We offer you the convenience of buying through a local partner, Peptide Solutions LLC who can import the shipment as well as prepay the customs duties and brokerage on your behalf and provide the convenience of a domestic sale.
Continue to Iris Biotech GmbHSend request to US distributorPublished on 13.02.2013
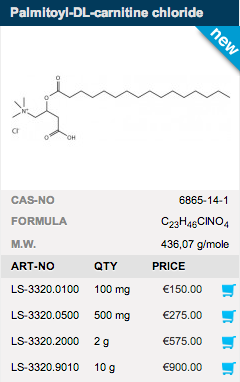
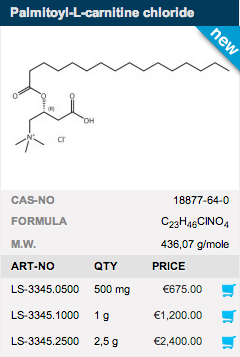
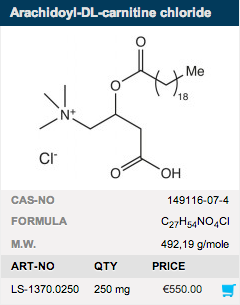
Long-chain acylcarnitines are well-known intermediates in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Palmitoyl carnitine is a very potent specific inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC), an important regulatory enzyme in several signal transduction cascades. Therefore, Palmitoyl carnitine has various physiological effects such as:
 |
 |
 |
References:
|